🧠 Function Call 深入解析笔记
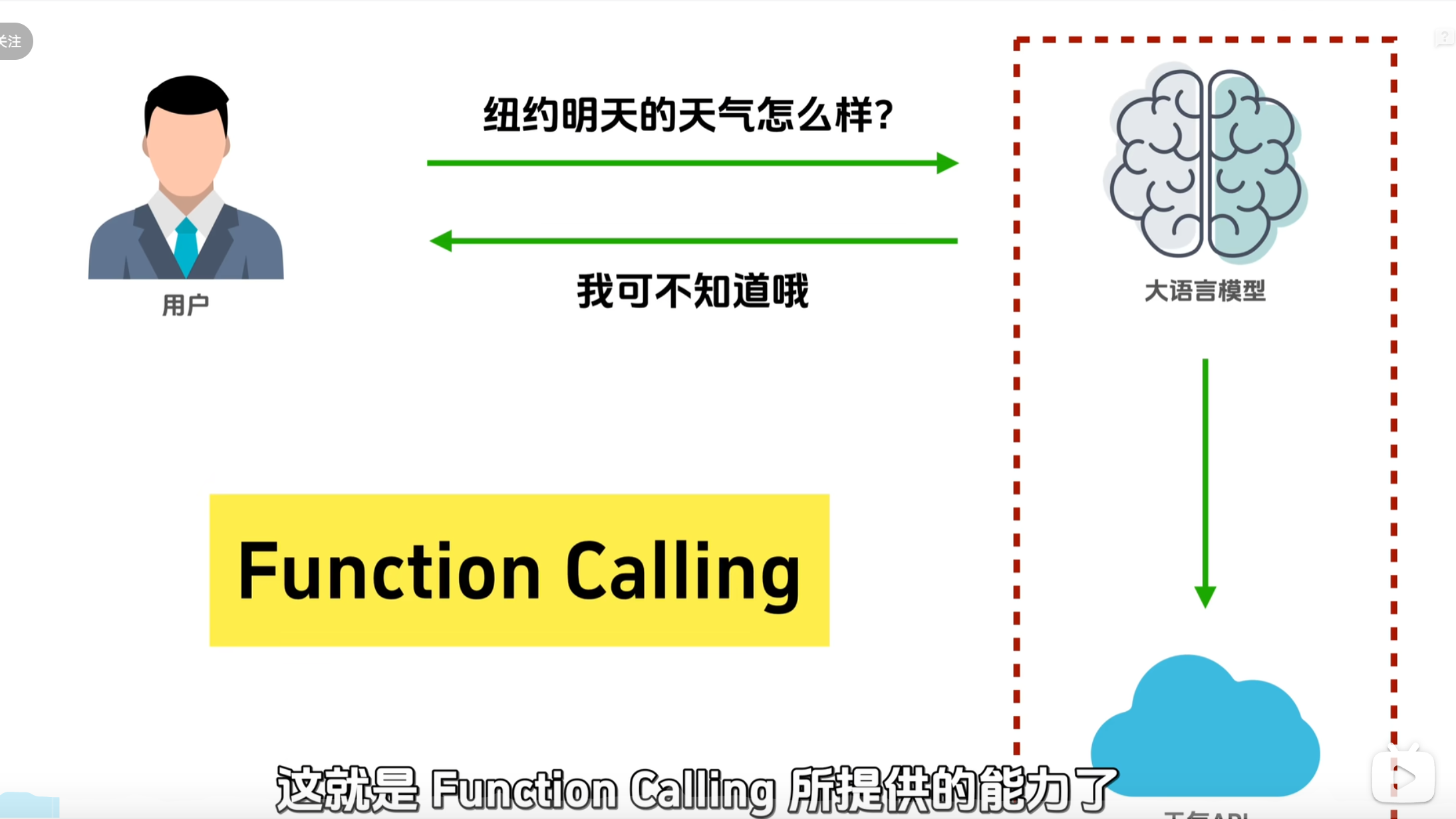
核心认知 :我们的请求包含"问题+工具箱",模型只有两个选择:自己给答案或调用工具(tool_calls),我们执行工具后再将结果返回模型获取最终答案
📂 完整流程与接口规范
1️⃣ 我们发送给模型的请求结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 { "messages" : [ { "role" : "user" , "content" : "明天纽约天气怎么样?" } ] , "tools" : [ { "name" : "search" , "description" : "联网搜索信息" , "parameters" : { "type" : "object" , "properties" : { "query" : { "type" : "string" , "description" : "搜索关键词" } } , "required" : [ "query" ] } } ] }
2️⃣ 模型返回的两种结果(关键!)
情况1️⃣: 直接回答(模型自己解决)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 { "choices" : [ { "message" : { "role" : "assistant" , "content" : "明天纽约多云,气温22-28℃" } } ] }
情况2️⃣: 工具调用(图片中的真实案例 👇)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 { "choices" : [ { "message" : { "role" : "assistant" , "content" : "" , "refusal" : null , "reasoning" : null , "tool_calls" : [ { "id" : "call_6wAqOpwRVz4D21U7I1g2pTBR" , "type" : "function" , "function" : { "name" : "search" , "arguments" : "{\"query\":\"New York weather forecast tomorrow\"}" } } ] } } ] }
🔧 工具调用处理流程
步骤1: 解析工具调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import jsontool_call = response['choices' ][0 ]['message' ]['tool_calls' ][0 ] tool_id = tool_call['id' ] tool_name = tool_call['function' ]['name' ] tool_args = json.loads(tool_call['function' ]['arguments' ])
步骤2: 执行工具
1 2 3 4 if tool_name == "search" : search_query = tool_args['query' ] result = execute_search(search_query)
步骤3: 包装结果返回模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 { "role" : "tool" , "tool_call_id" : "call_6wAqOpwRVz4D21U7I1g2pTBR" , "name" : "search" , "content" : "{\"temperature\":26,\"conditions\":\"sunny\"}" }
步骤4: 获取最终回答
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 { "choices" : [ { "message" : { "role" : "assistant" , "content" : "纽约明天晴天☀️,气温26℃,适合户外活动!" } } ] }
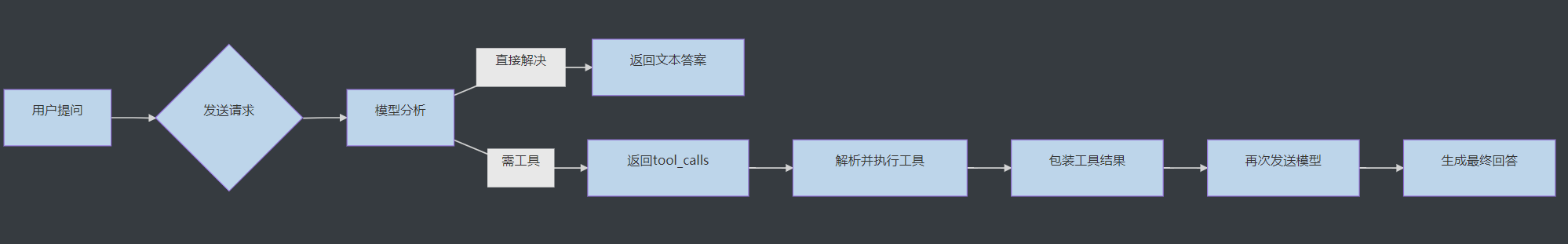
📊 核心调用流程图
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 graph LR A[用户提问] --> B{发送请求} B --> C[模型分析] C -->|直接解决| D[返回文本答案] C -->|需工具| E[返回tool_calls] E --> F[解析并执行工具] F --> G[包装工具结果] G --> H[再次发送模型] H --> I[生成最终回答]
💡 关键学习点(按图片信息总结)
tool_calls 是黄金信号
content 为空字符串:表示需要调用工具refusal和reasoning为null:表示无拒绝理由绿色参数字符串:在JSON中以\"形式转义双引号
参数解析特别注意
1 2 3 4 5 arguments = "{\"query\":\"New York weather forecast tomorrow\"}" params = json.loads(arguments)
调用链必须完整
返回工具结果时:tool_call_id 必须匹配原始调用ID
工具名称:必须和请求中定义的一致(区分大小写)
真实案例标识符
1 2 "id" : "call_6wAqOpwRVz4D21U7I1g2pTBR" "arguments" : "{\"query\":\"...\"}"
总结 :理解tool_calls结构 → 精确提取参数 → 正确返回工具结果 → 获得最终答案
Function call 概括
调用外部接口
参考链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15YJTzkENC/?spm_id_from=333.1007.tianma.1-2-2.click&vd_source=82dc2acb60a90c43a2ac0d4023a2cd34
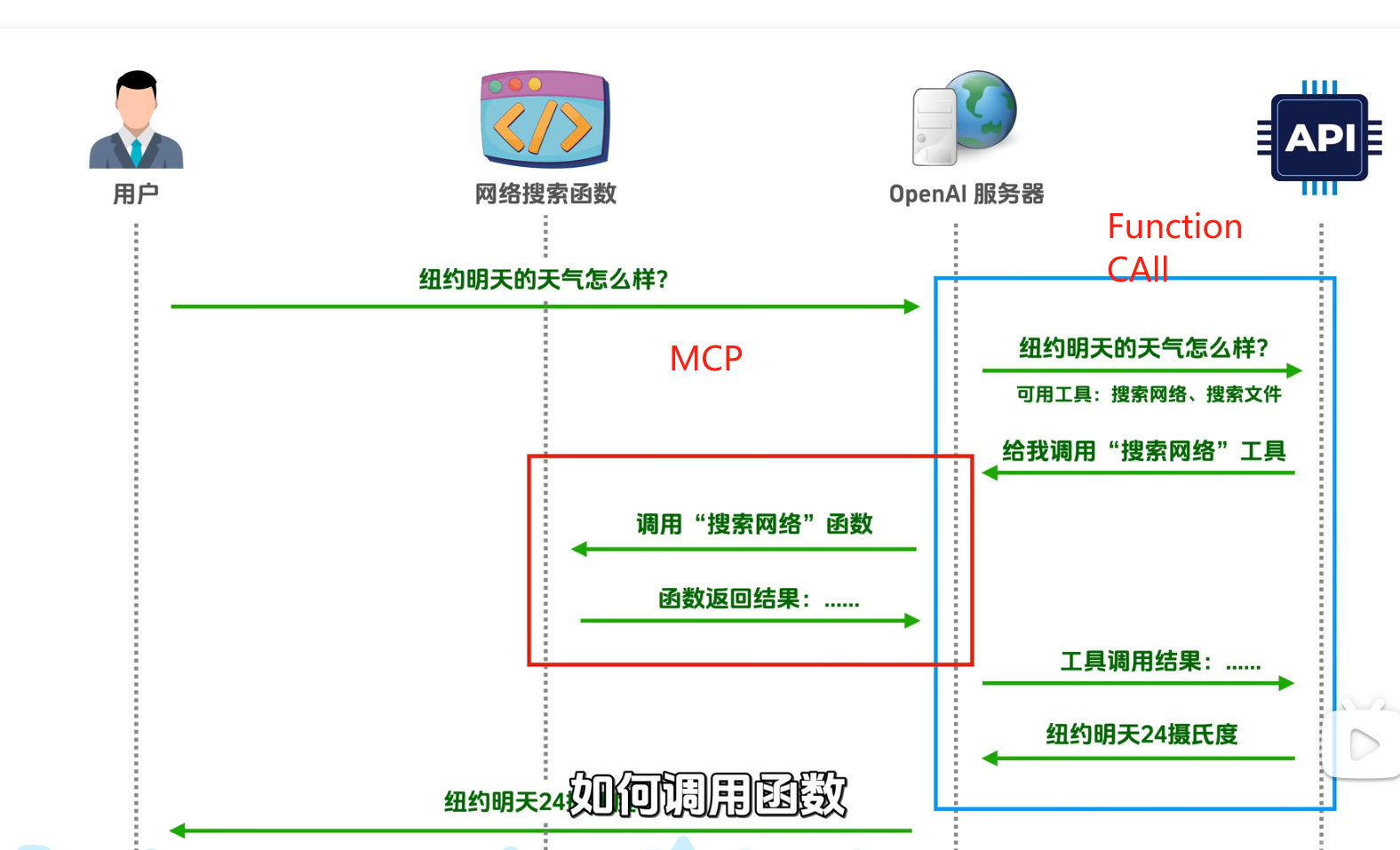
Function call和MCP 位于不同的位置
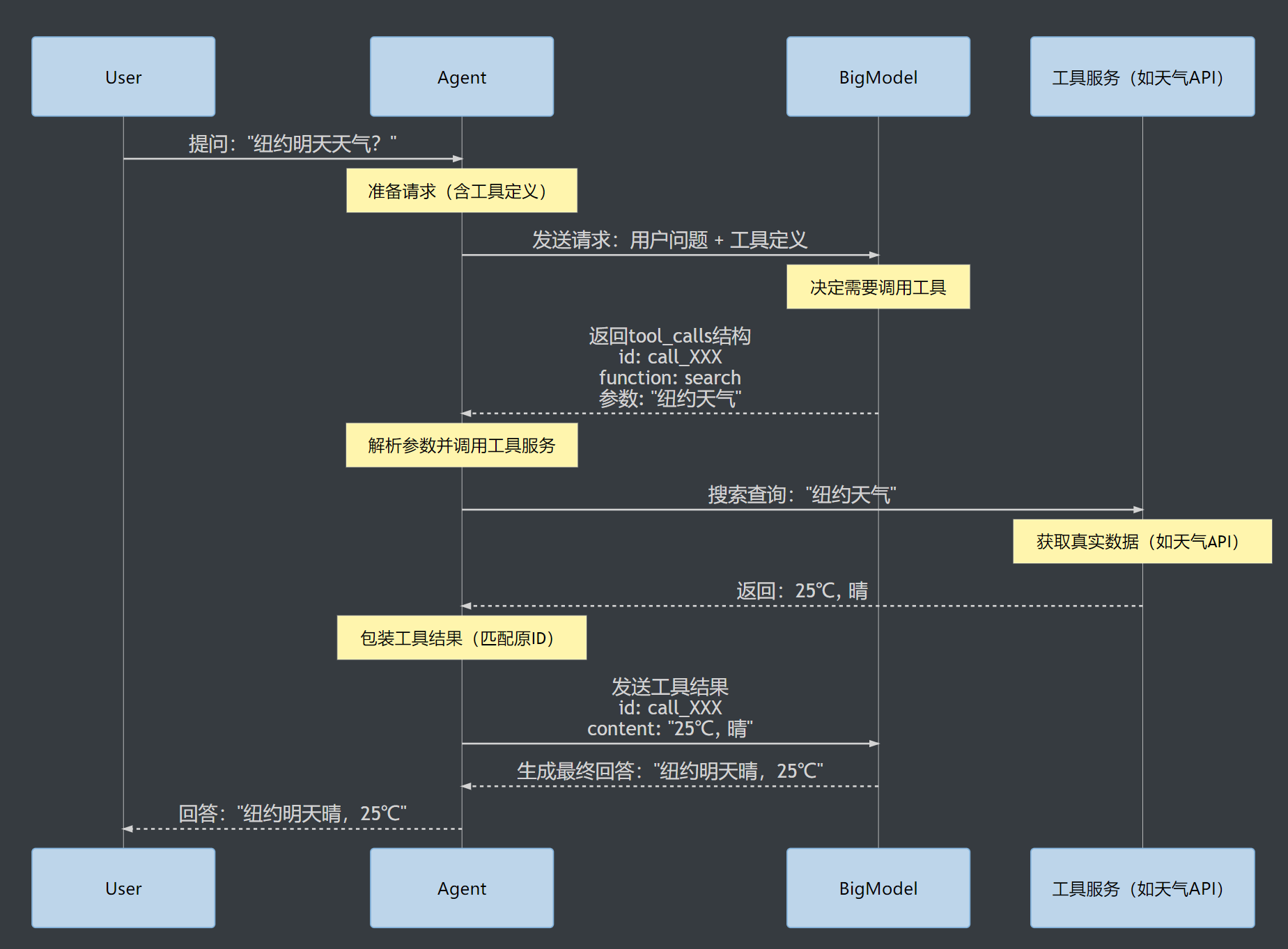
🌐 Function Call 工具调用全流程指南
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 sequenceDiagram participant User participant Agent participant BigModel participant MCP as 工具服务(如天气API) User->>Agent: 提问:"纽约明天天气?" Note over Agent: 准备请求(含工具定义) Agent->>BigModel: 发送请求:用户问题 + 工具定义 Note over BigModel: 决定需要调用工具 BigModel-->>Agent: 返回tool_calls结构<br/>id: call_XXX<br/>function: search<br/>参数: "纽约天气" Note over Agent: 解析参数并调用工具服务 Agent->>MCP: 搜索查询:"纽约天气" Note over MCP: 获取真实数据(如天气API) MCP-->>Agent: 返回:25℃, 晴 Note over Agent: 包装工具结果(匹配原ID) Agent->>BigModel: 发送工具结果<br/>id: call_XXX<br/>content: "25℃, 晴" BigModel-->>Agent: 生成最终回答:"纽约明天晴,25℃" Agent-->>User: 回答:"纽约明天晴,25℃"
🧩 关键要素说明
1️⃣ 工具定义规范(来自您图片中的search工具)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 { "name" : "search" , "description" : "搜索天气信息" , "parameters" : { "type" : "object" , "properties" : { "query" : { "type" : "string" } } , "required" : [ "query" ] } }
2️⃣ 工具调用参数解析(重点!)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import jsonresponse_data = { "tool_calls" : [{ "function" : { "arguments" : "{\\" query\\":\\" 纽约天气\\"}" } }] } arguments_str = response_data["tool_calls" ][0 ]["function" ]["arguments" ] arguments_dict = json.loads(arguments_str) print (arguments_dict["query" ])
3️⃣ 工具结果返回规范
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 tool_response = { "role" : "tool" , "tool_call_id" : "call_XXX" , "content" : json.dumps({ "temperature" : 25 , "conditions" : "晴" }) }
🔧 完整实现代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 import requestsimport jsonclass FunctionCallAgent : def __init__ (self, api_key ): self .api_key = api_key self .base_url = "https://api.example.com/v1/chat/completions" self .history = [] def call_big_model (self, messages, tools=None ): headers = { "Authorization" : f"Bearer {self.api_key} " , "Content-Type" : "application/json" } payload = { "model" : "gpt-4-turbo" , "messages" : messages, "tools" : tools } try : response = requests.post( self .base_url, json=payload, headers=headers, timeout=10 ) return response.json() except Exception as e: print (f"API请求失败: {str (e)} " ) return None def process_query (self, query ): self .history.append({"role" : "user" , "content" : query}) tools = [{ "type" : "function" , "function" : { "name" : "search" , "description" : "搜索天气信息" , "parameters" : { "type" : "object" , "properties" : { "query" : {"type" : "string" } }, "required" : ["query" ] } } }] response = self .call_big_model(self .history, tools) if not response: return "服务不可用" message = response["choices" ][0 ]["message" ] self .history.append(message) if "tool_calls" in message: tool_call = message["tool_calls" ][0 ] call_id = tool_call["id" ] func_name = tool_call["function" ]["name" ] args_str = tool_call["function" ]["arguments" ] try : args_dict = json.loads(args_str) except json.JSONDecodeError: args_dict = {"query" : "解析失败" } if func_name == "search" : weather = self .execute_search(args_dict["query" ]) else : weather = {"error" : "未知工具" } tool_response = { "role" : "tool" , "tool_call_id" : call_id, "content" : json.dumps(weather) } self .history.append(tool_response) final_response = self .call_big_model(self .history) answer = final_response["choices" ][0 ]["message" ]["content" ] return answer return message["content" ] def execute_search (self, query ): """实际查询天气API的代码""" return {"temperature" : 25 , "conditions" : "晴" } agent = FunctionCallAgent(api_key="your-api-key" ) result = agent.process_query("纽约明天天气?" ) print ("最终回答:" , result)
📚 完整文档使用说明
使用时序图 :
复制上方Mermaid代码到支持Mermaid的Markdown编辑器
推荐使用VS Code + Mermaid插件 或 Typora
使用代码 :
替换api_key="your-api-key"为您的大模型API密钥
根据实际需求实现execute_search方法
适配您图片中的信息 :
严格遵循黄色标记的工具列表结构
正确处理arguments的双重转义格式
保持ID匹配机制
竭力的进入安息。喜欢赞美和敬拜,喜欢在经文中看到主耶稣,有志同道合的朋友可以加微信私聊:xingxiliang。